Factors Affecting Nurses’workplace Stress Inyowari Hospital Of Sentani District Jayapura
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.18502/kss.v1i1.451Abstract
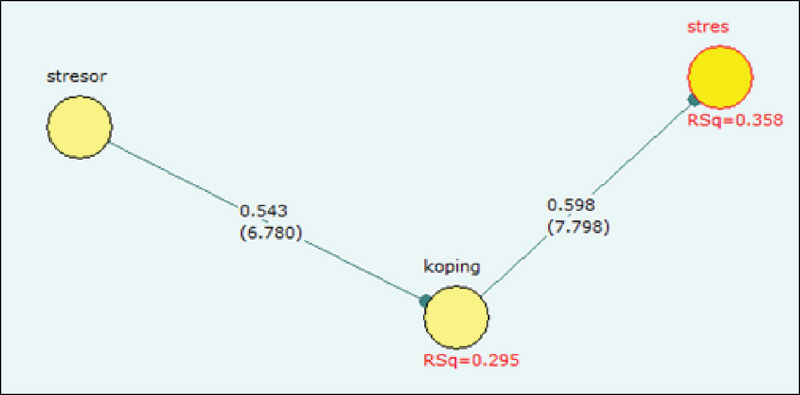
Work stress is distress experienced by individuals in the face of work caused by the stressors of work environment factors such as physical environment, organizational systems and individuals. The research objective was to determine what factors are causing stress in nurses who work in Hospital. This research used explanatory research with cross sectional approach. These samples included 55 nurses in hospitalization ward. The instrument of this study is a questionnaire. The data were analyzed using descriptive statistics, bivariate analysis using chi square test, and multivariate analysis using Structural Equation Modeling (SEM).The results of univariate analysis showed that the nurses stress of 61.8% found in the characteristics of the age of 21-40 years (87.3%), female (85.5%) education level Diploma Nurses (74.5%), has a work period ≤ 5 years (60.0%), the status of civil servants (54.5%), were married (76.4%), and working in the internal ward (30.9%), with a personality type extrovert (70.9%). The level of stress is often the case that self esteem (87.3%), despair and a sense of worthlessness (80%), success (72.7%) and interest (72.7%). The bivariate analysis showed that, Stressors that significant with stress were: support, organization, interaction with the p-value (0.012 <0.05). The coping mechanisms were social support as an emotional reason the value of p-value(0.040 <0.05).The closeness to the religious p-value(0.002 <0.05) significantly between closeness to religion with work stress. The most factors that have an effect on the coping mechanisms Equtional Modeling Structural testing with loading value of 0.598 and 7.798 correlated, which means that the coping mechanisms 7 times have influence to reduce stress in the workplace.
Keywords: workplace stress, nurse, patient wards
References
R. I. Allen, E. G. Lambert, and S. Pasupuleti, Cluse-Tolar, The Impact for Job
Characteristic on Sosial and Human Service Wokers, Sosial Work & Society, Ventura, LA, 2004.
K. Appleton, A. House, and A. Dowell, A survey of job satisfaction, sources of stress and psychological symptoms among general practitioners in Leeds, Br J Gen Pract, 48, 1059–1063, (1998).
K. Azam, M. Pourmahabadian, and A. Rezaeian, Work Related Stres Chracteristic on Correctional Staff Job Stress, Appl Psychol Crim Justice, (2005).
T. A. Beehr, 1978, Job stress, Employe Health and Organization Development, USA, Havard Business Review.
J. A. Blumenyhal, E. T. Thyrum, and W. C. Siegel, Contribution of Job Strin, Job Status and Marital Status to Laboratory and Ambulatory Blood Pressure in Patients with Mild Hypertension, Journal of Psychosomatic Reseach, (1995).
C. L. Cooper and R. Payne, Coping and Consequenses of Stress at Work, Wiley, New York, 1988.
SPSS 20, Analisis Data Statistik, Andi Yogyakarta, (2012).
Europen Foundation for the Improvement of Living and Working Conditions Workrelated Stres, (2007).
Frasser Stress dan KepuasanKerja, PT. Pustaka Binawan Presindo, Jakarta, 1992.
C. S. Gatson, The Relationship between Education and Police Stress, Bachelors Degree versus High School (Thesis), Marshall University.
C. Hudack and B. M. Gallo, Keperawatan Kritis, Pendekatan Holisstik, EGC, Jakarta, 1997.
H. Nurjazuli, Paradigma Baru Dalam Analisis Data Penelitian Structural Equation Modeling dengan Visual Partial Least Square, Universitas Diponegoro, 2012.
R. Hodson, Group Relations at Work Splidarty, Conflict and Relations with Management Work and Occupational, J Appl Psychol, (1997).
E. G. Lambert, S. D. Camp, C. Edward, and W. G. Saylor, Gone Tomorrow, Back Again the Next Day, Absenteeism and its Antecedents among Federal Correctional staff, Journal of Criminical Justice, (2005).
T. Looker and O. Gregson, Managing Stress, Peneribit Baca, Yogyakarta, 2005.
F. Jones and J. Briggt, 2001, Stress, Myth, Theory and Research, Harlow, Prentice Hall (English), 2001.
D. Katz and R. L. Kahn, The social psychology of organization, John Willey and Sons, New York, 2nd ed edition, 1978.
M. Muclas, Perilaku Organisasi 3, Program Pendidikan Pasca Sarjana Magister Manajemen Rumah Sakit UGM, 1999.
The Prevalence Of Psytchological Distress And Associated Factors Among People Living With Aids Anttending Antiretroviral Therapy in Mzuzu, Malawi, (2006).
Notoadmodjo S., Reseach Health Method, PT Rineka Cipta, 2005.
E. S. Pallesen, Work-related Stres and Health among Hotel Employees in Malmo, Tesis, 2007.
K. R. Parkes, Locus of Control, Cognitive Appraisal, and Coping in Stressful Episodes, J Pers Soc Psychol, (1955).
Job Related Stress, Personality, Social Support And Burnout Among College Of Education Lecture, 4 thregional conference on Higher Education Research For Sustainable Development In Africa Organized By Higher Education Research And Policy Network (HERPNET) in collaboration with, Iternational University, Kampala, (2009).
A. Sobur, PsikologiUmum, Pustaka Setia, Bandung, 2003.
P. Suwarno, Hubungan Masa Kerja dengan Stres Kerja pada Pustakawan Perpustakaan Universitas Gadjah Mada, Yogyakarta.Majalah Berkala Ilmu Perpustakaan dan Informasi, 2006.
C. F. Sharpley, R. Reynolds, A. Acosta, and J. K. Dua, The Presense, Nature And Effects Of Job Stress On Physical And Physicological Health At A Large, Australian University, J Educ Adm, (1996).
Tarwaka, Ergonomi Industri, Harapan Press, Surakarta, 2010.
Tee Soo Kim, Stres Kerja di Kalangan Guru Aliran Teknik di Sekolah Menengah Teknik Negeri Johor, Melaka dan Negeri Sembilan, Tesis, Universitas Teknologi Malaysia, 2006.
H. L. Tosi, J. R. Rizzo, and S. J. Caroll, in Managing Organizational Bahavior, Harper Collins Publisher, 2nd ed edition, 1990.
G. Vanagas, S. B. Axelsson, and V. Vanagiene, (2004).
G. Vanagas, S. B. Axelsson, and V. Vanagiene, in Do Age, The Factors Associated to Psychososial Stress Among General Practitioners in Lithuania, BioMed Central Health Service Research, Sweden, 2005.
N. P. Vokic and A. Bogdanic, Individual Differences and Occupational Stress Perceived, a Croatian survey (2007).
B. Wantoro, Stress Kerja, Majalah Hiperkes dan Keselamatan Kerja, 1999, Jakarta.
T. W. Whitley, E. J. Allison, M. E. Gallery, R. A. Cokington, P. Gaudry, and J. Heyworth, Work-Related Stress and Depression Among Practicing Emergency Physician: An International Study, Ann Emerg Med, (1993).