Morphological And Anatomical Structure Of Red Fruit (Pandanus Conoideus Lam.)
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.18502/kss.v1i1.432Abstract
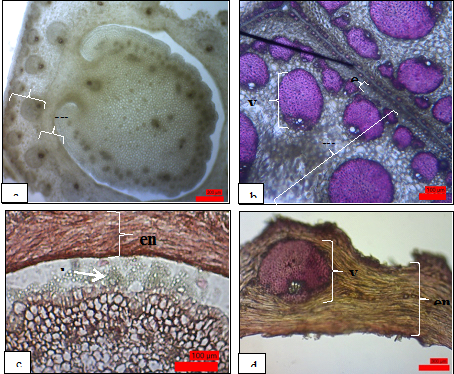
Red fruit (Pandanus conoideus Lam.) is one of the plant species in Pandanacea family. Moreover, it is also used as food, medicines, and dyes in Eastern part of Indonesia. For the local people in Papua, however, it is difficult to grow the red fruit using seed propagation due to the seed dormancy. In this study, we investigated the morphological and anatomical structure of the red fruit seeds. We conducted the study by observing the morphological and anatomical structure of the red fruit seeds and its seed dormancy. The study revealed that the red fruit drupe was divided into exocarp, mesocarp and endocarp layers. Anatomical analysis indicated that the seed coat consisted of parenchyma and lignin-walled cells. The inner layer of the seed coat was covered by mucilaginous, blockage and per carp. The endosperm consisted of starch containing parenchyma cells and small sized embryos that contained small parenchyma cells.
Keywords: Red Fruit, Drupe, Structure
References
A. VF. Bobrov, 2008, Red Fruit. CV Bali Spot Internasional Co. Ltd., Diakses Maret, 2012 www.buah-merah.info, (2012).
J. D. Bewley and M. Black, Seeds: Physiology of Development and Germination, Plenum Press, New York, 1994.
A. V. F. Bobrov, D. H. Lorence, M. S. Romanov, and E. S. Romanova, Fruit Development and Pericarp Structure in Nypa fruticans Wurmb (Arecaceae): A Comparison With Other Palms, Int J Plant Sci, 173, 751–766, (2012).
F. Essig, A Systematic Histological Study of Palm Fruit I, The Ptychosperma alliance, Syst Bot, 2, 151–168, (1977).
A. Fahn, Plant Anatomy, Gadjah Mada University Press, 1995.
L. Limbongan and A. Malik, Development Opportunities of Red Fruit (Pandanus conoideus Lam.) in Papua Province, Jurnal Litbang Pertanian, 28, 135–141, (2009).
M. Makaruku [8] A. C. Martin, The Comparative Internal Morphology of Seeds, Am Midl Nat, 36, 513– 660, (1946).
M. S. Romanov, A. V. Bobrov, D. SA. Wijesundara, and E. S. Romanova, Pericarp development and fruit structure in borassoid palms (Arecaceae-Coryphoideae- Borasseae), Ann Bot (Lond), 108, 1489–1502, (2011).
S. Sadjad, Development Guide Plant Seed Quality of Forestry in Indonesia, Forestry Seeding Center Project Reforestation and Rehabilitation Directorate General Directorate of Forestry, 1980.
M. J. Sadsoeitoeboen, Pandanaceae: Aspects of Botany and Ethnobotany in the Life Tribe Arfak in Irian Jaya. Unpublished data (1999).
S. Sutarno, Plants Producing Natural Color and Utilization of the Life Tribe Meyah in the Village Yoom Nuni Manokwari, Unpublished data (2001).
R. Z. Tambunan, Soaking Test Effect in Different Water Temperature on Germination of Red Fruit Seed length (Pandanus conoideus Lam.), Unpublished data (2005).
B. T. W. Wiryanta, Potency and Benefits of Red Fruit, Agromedia, Jakarta, 2005.